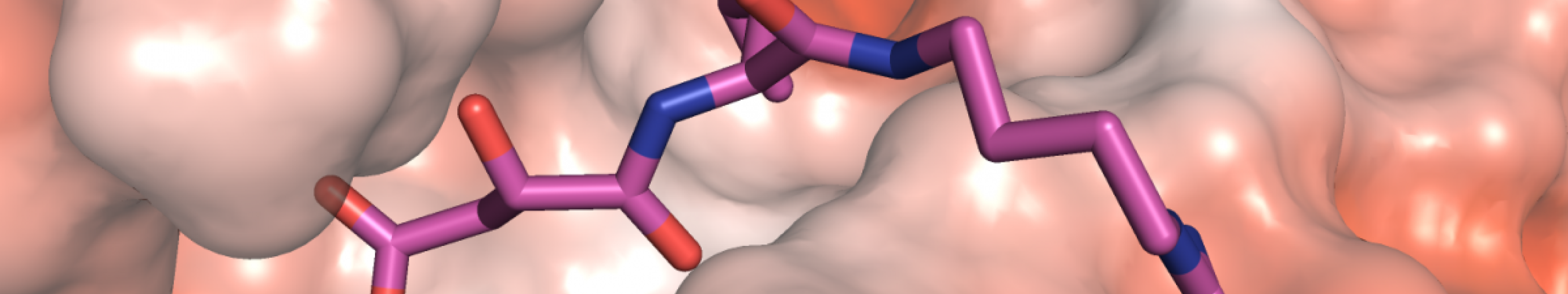
Drug design refers to the inventive process of creating new compounds and medications based on our knowledge of a biological target. Often, this biological target is a protein that may be inhibited to provide a therapeutic effect. A detailed understanding of a protein’s structure and function is often required in the design of novel inhibitors. The Mahajan laboratory utilizes virtual, or computer-aided, drug design methods to model new compounds that are complementary to a target protein’s shape and charge. These protein-inhibitor complexes are modeled on our lab’s parallel computing system and can be visualized in three-dimensions on 3D monitors, providing an in-depth view of these molecular interactions. Virtually-designed compounds are then synthesized in collaboration with Stanford’s Medicinal Chemistry Knowledge Center for testing in biochemical and cellular assays.
Mahajan Laboratories
Department of Ophthalmology